Remote Access with OpenSSH and VNC
This section describes how
to access the StarHPC 4 node compute cluster
remotely. Below are general instructions for each
platform. For all platforms, you will need to install
openssh and tightvnc. The instructions below merely
give the links for any software needed. On some
platforms openssh may already be installed which will
be mentioned below if that is the case. If you need
further assistance in addition to what's below
contact: star *at* mit.edu
NOTE: For all platforms, you need to
go here
to get a username, password, hostname, and port to
connect to. (MIT
certificates required). These will be referenced in
the instructions as $username,
$password,
$hostname, and
$port.
Windows | Mac | Athena/Redhat/Fedora | Ubuntu | Gentoo |
Archlinux
Windows (remote)
- Go here
to get a username, password, hostname, and port to
connect to (MIT
certificates required)
- Download and install
putty into your C:\WINDOWS\System32 directory.
Make sure you install into C:\WINDOWS\System32
instead of C:\Program Files\Putty

- Download and install
tightvnc
- Go to Start → Run, type “cmd” in the “Run” dialog
and press return
- In the terminal window run substituting the
$username,
$password,
$hostname, and
$port from here
(MITcertificates
required):
putty -ssh -L
$port:localhost:$port $username@$hostname
- Type in your $password from
above when prompted and minimize the terminal after
you're logged in.
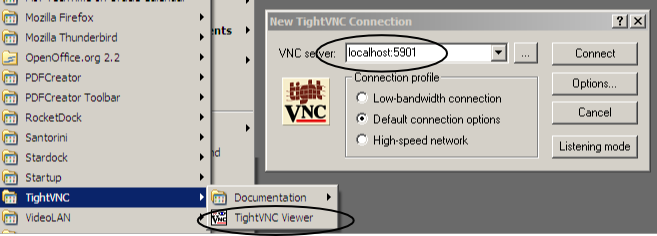
- Open tightvnc viewer and point it to
localhost:$port with the
$portretrieved from the first step
(in the image below, the port retrieved from above
was 5901; substitute the port you retrieve from step
1 for 5901).
Return to top
Mac (remote)
- Go here
to get a username, password, hostname, and port to
connect to (MIT
certificates required).
- Download and install Chicken of VNC for Mac OSX
from
here.
- Open a terminal and run substituting the
$username, $password,
$hostname, and
$port from here(MIT
certificates required):
ssh
-L $port:localhost:$port
$username@$hostname
- Type in your $password from
above when prompted and minimize the terminal after
you're logged in.
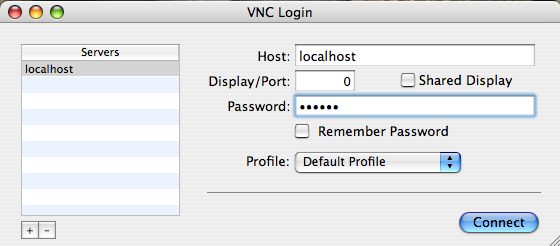
- Open Chicken of VNC and set the host field to
“localhost” and the port field to
$port retrieved from the first
step.
Return to top
Linux (remote)
Athena/Redhat/Fedora
- Go here
to get a username, password, hostname, and port to
connect to (MIT
certificates required).
- Download tightvnc
here.
- Install the tightvnc rpm you just downloaded by
running as root:
rpm
-i tightvnc-1.3.9-1.i386.rpm
- Open a terminal and run substituting the
$username, $password,
$hostname, and
$port from here
(MIT certificates required):
ssh
-L $port:localhost:$port
$username@$hostname
- Type in your $password from
above when prompted and minimize the terminal after
you're logged in.
- Open a terminal and run:
vncviewer
localhost:$port
Return to top
Ubuntu
- Go here
to get a username, password, hostname, and port to
connect to (MIT certificates required).
- Install tightvnc by running:
-
sudo apt-get
install xtightvncviewer
- Open a terminal and run substituting the
$username, $password,
$hostname, and
$port from here
(MIT certificates required):
ssh
-L $port:localhost:$port
$username@$hostname
- Type in your $password from
above when prompted and minimize the terminal after
you're logged in.
- Open a terminal and run:
vncviewer
localhost:$port
Return to top
Gentoo
- Go here
to get a username, password, hostname, and port to
connect to (MIT certificates required).
- Install tightvnc by running as root:
emerge -va
tightvnc
- Open a terminal and run substituting the
$username, $password,
$hostname, and
$port from here
(MIT certificates required):
ssh
-L $port:localhost:$port
$username@$hostname
- Type in your $password from
above when prompted and minimize the terminal after
you're logged in.
- Open a terminal and run:
vncviewer
localhost:$port
Return to top
Archlinux
- Go here
to get a username, password, hostname, and port to
connect to (MIT certificates required).
- Install tightvnc by running as root:
pacman -S
tightvnc
- Open a terminal and run substituting the
$username, $password,
$hostname, and
$port from here
(MIT certificates required):
ssh
-L $port:localhost:$port
$username@$hostname
- Type in your $password from
above when prompted and minimize the terminal after
you're logged in.
- Open a terminal and run:
vncviewer
localhost:$port
Return to top


