This load balancer grows and shrinks a Sun Grid Engine cluster according to the length of the cluster’s job queue. When the cluster is heavily loaded and processing a long job queue, ELB can gradually add more nodes, up to the specified max_nodes, to distribute the work and improve throughput. When the queue becomes empty, ELB can remove idle nodes in order to save money. The cluster will shrink down to one node (the master), terminating all of the other nodes as they become idle.
Goals
To use the Elastic Load Balancer, you can start it from the command line:
starcluster loadbalance cluster_tag
or
starcluster bal cluster_tag
This will start the load balancer in an infinite loop. It can be terminated by pressing CTRL-C.
At this time, all of the parameters are stored in the file starcluster/balancer/sge/__init__.py with the appropriate descriptions. Before release, those configuration options will be moved to the standard starcluster configuration file.
There is a polling loop, default is 60 seconds, set in the configuration of the load balancer. Every 60 seconds, the load balancer will connect to the cluster, obtain statistics from Sun Grid Engine, and decide what to do about the job queue. ELB deals only with the queue length and active machines.
ELB does not examine the load on any of the hosts. If we had the ability to migrate jobs from an overloaded host to an idle host, then we would spend more time looking at individual hosts’ system load. However, since job migration is out of the scope of this project and starcluster in general, we do not look at system load.
This diagram illustrates the decisions that ELB will make in each loop:
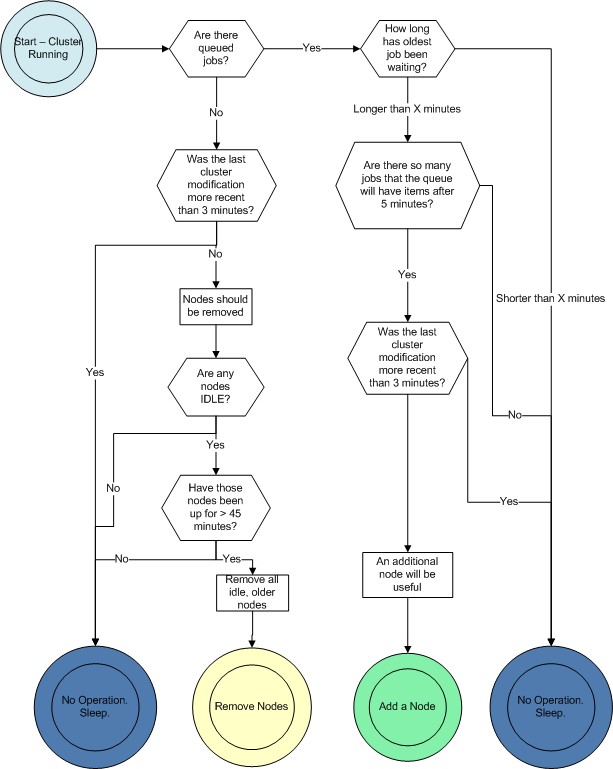
As mentioned before, the load balancer will loop every 60 seconds, collecting statistics to make intelligent decisions about when to add nodes.
Criteria for Adding a Node
A node will be added when all of the following criteria have been met:
There are jobs in the queued waiting (SGE’s moniker is ‘qw’) state
The longest queued job has been waiting for more than 15 minutes
set in the configuration file.
A user can set the number of nodes to be added per iteration. For instance, if the user wanted to add 1 node per iteration, which is standard and a recommended practice, they would set the add_nodes_per_iteration parameter to 1. If the user wanted two nodes to be added per iteration, that parameter should be set to 2, and the cluster would grow at a faster rate, consequently incurring higher charges from Amazon.com.
Criteria for Removing a Node
A node will be removed when all of the following criteria have been met:
Each node in the cluster will be analyzed in turn, and any and all nodes meeting the above criteria will be terminated in that polling loop. The entire cluster need not be idle for a node to be terminated: If Node001 is working on a job, but Node002 is idle and there are no queued waiting jobs, Node002 is a candidate for termination.
The 45 Minutes Past the Hour Rule
Since Amazon charges by the hour, we are assuming that you have already paid for a full hour of server time. It would be wasteful to turn it off the moment it becomes idle. By keeping that node up for 45 minutes, we allow for it to complete the maximum workload from the queue, and use 75% of the hour you have already paid for.
Leaving a node up for this amount of time also increases the stability of the cluster. It is detrimental to the cluster and wasteful to be continuosly adding and removing nodes.
The Process of Adding a Node
Adding a new node is a multi-stage process:
The Process of Removing a Node
Removing a node is also a multi-stage process:
Because the node is immediately removed from SGE, and it seems like SGE takes about 15 seconds between a qsub command and a node beginning execution of a job, this makes it very unlikely that a job will be started on a host as it is going down. There is a very small window of time within which this could happen.